Application
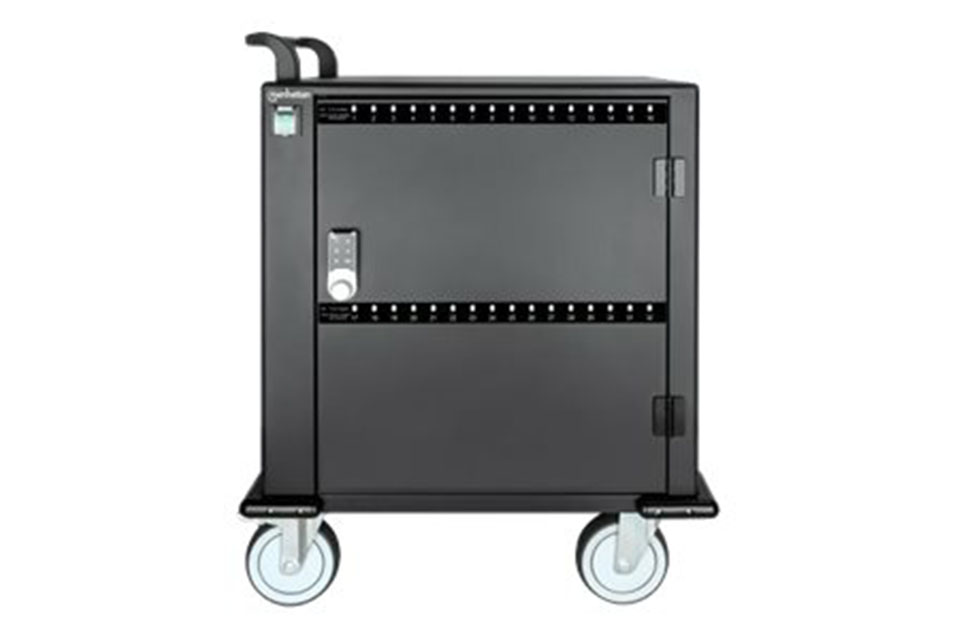

Charging cabinets are vital in education, government, enterprise IT, and healthcare—enabling organized, secure, and simultaneous charging of multiple portable devices such as laptops, tablets, and phones.
Key Benefits
1. Lockable, tamper-proof doors for security
2. Simultaneous multi-device charging (USB/AC ports)
3. Overvoltage and surge protection
4. Wall-mounted or mobile (with caster wheels)
Use Cases
1. School device storage and charging (1:1 laptop programs)
2. Hospital nurse stations
3. Conference and training centers
4. Retail POS tablet docking
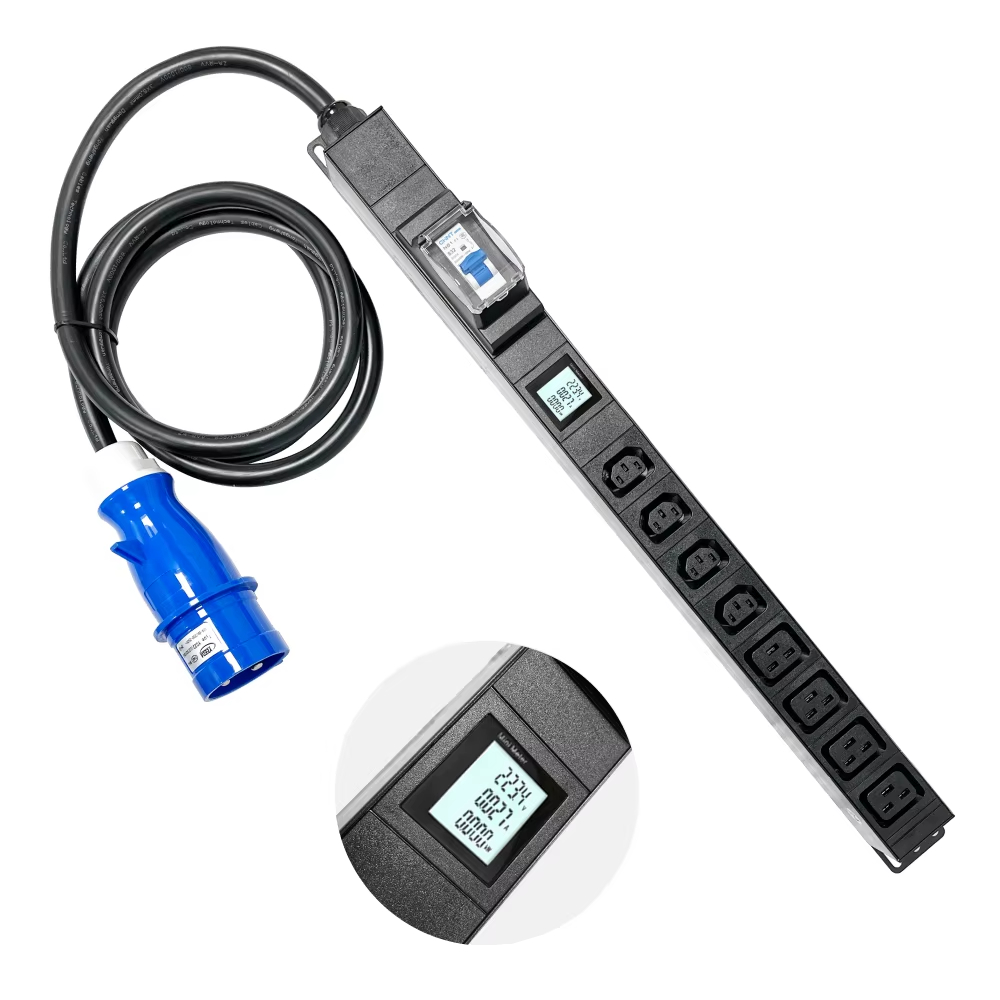
Smart PDUs go beyond traditional outlet strips by offering real-time energy monitoring, environmental sensing, and remote power management for server racks and telecom environments.
Key Benefits
1. IP-based remote outlet switching
2. Current, voltage, and energy metering
3. SNMP, Modbus, and RESTful API support
4. Rackmount and vertical designs
Use Cases
1. Colocation data centers requiring per-client billing
2. Lights-out server rooms and edge computing sites
3. Equipment testing and automated labs
4. Remote rebooting of power-hungry devices
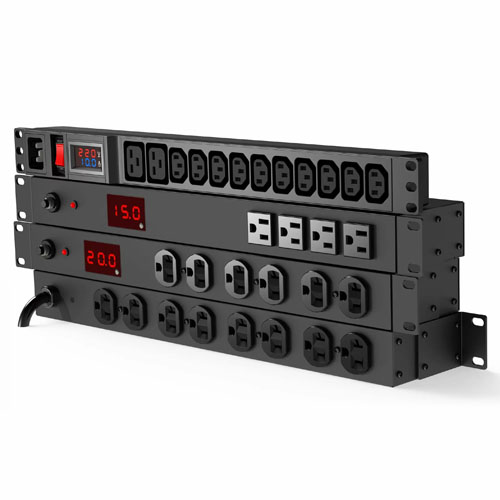


High-power PDUs are engineered for dense compute environments like AI clusters, crypto mining farms, and HPC installations—delivering scalable, high-amperage energy safely.
Key Benefits
1. Three-phase power support
2. Up to 400A rating with robust cable lugs
3. Load balancing and failover designs
4. High-heat tolerance for harsh environments
Use Cases
1. High-density server farms
2. AI/ML supercomputers
3. Modular container data centers
4. Broadcast and rendering farms
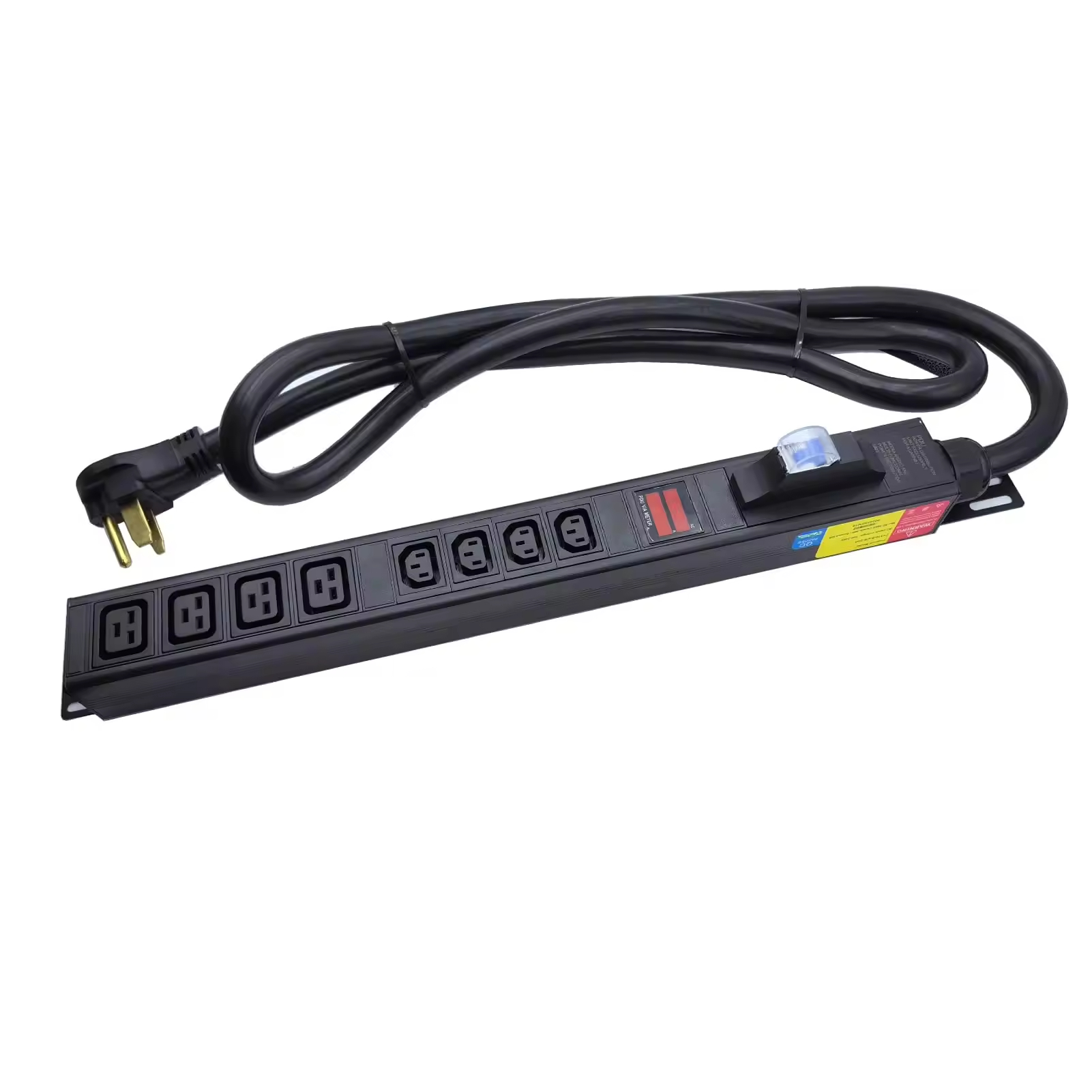
Reliable, no-frills PDUs for cost-effective power delivery across standard IT equipment, labs, and telecom closets.
Key Benefits
1. Compact and plug-and-play
2. Horizonal/vertical rackmount
3. Circuit breakers for surge protection
4. Variety of outlet configurations (C13, C19, NEMA)
Use Cases
1. SMB server rooms
2. Networking closets
3. Remote backup locations
4. Industrial test benches


Switchgear protects and controls electrical equipment in medium- to high-voltage power distribution systems. Critical in utility, industrial, and data center power delivery.
Key Benefits
1. Short-circuit and overload protection
2. Isolated busbars and breakers
3. Air-insulated, gas-insulated (GIS), or hybrid designs
4. Arc-flash mitigation and modular expandability
Use Cases
1. Electrical substations
2. Large-scale manufacturing plants
3. Data center transformer rooms
4. Airport and metro utility control rooms
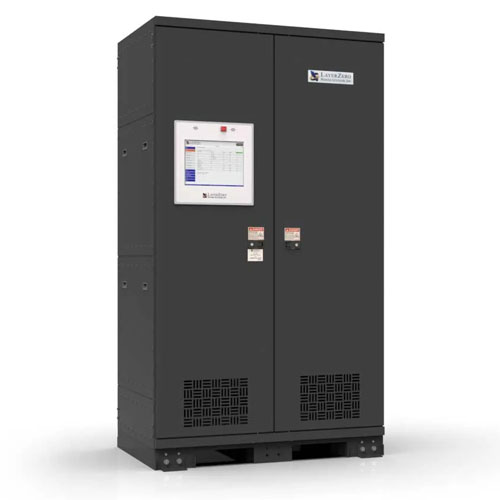
STS units provide seamless, near-instantaneous switching between dual power sources, ensuring power continuity for mission-critical IT loads.
Key Benefits
1. Transfers in less than 4ms (no system drop)
2. Monitors input phase and voltage in real-time
3. SCR-based switching for reliability
4. Dual-source input and output redundancy
Use Cases
1. Tier 3 and 4 data centers
2. Surgical operating rooms
3. Financial trading server racks
4. Telco central offices
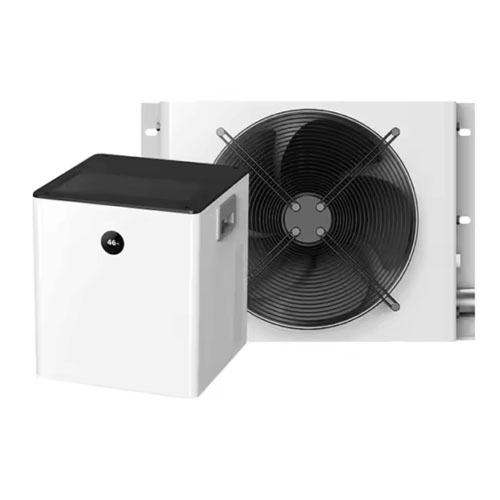


Immersion cooling submerges servers in dielectric fluid to remove heat at the source—reducing cooling costs, increasing efficiency, and supporting high-density deployments.
Key Benefits
1. 100% server heat absorption
2. No fans required—near silent operation
3. PUE as low as 1.02
4. Compatible with GPU, ASIC, and FPGA deployments
Use Cases
1. Crypto mining farms
2. AI/HPC datacenters
3. Edge nodes in warm climates
4. Energy-conscious data centers
Unlike full immersion, liquid cooling cabinets use cold plates or direct-to-chip cooling paired with closed-loop coolant systems to maintain thermal performance.
Key Benefits
1. Rack-level cooling with minimal air involvement
2. Eliminates airflow contamination
3. Closed-loop refrigerant or water systems
4. Integration-ready with standard racks
Use Cases
1. AI clusters running 24/7
2. Government or military compute facilities
3. ESG-aligned enterprise cloud centers
4. ESG-aligned enterprise cloud centers